投資の状況について
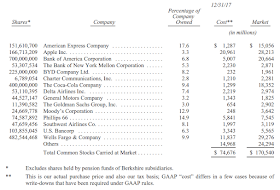
以下の表は、当社が投資した普通株のうち、年末時点で市場評価額が大きかった15件を並べたものです。ただしクラフト・ハインツ社の3億2,544万2,152株は含んでいません。バークシャーは同社の支配会社に名を連ねているので、「持分」法によって会計報告することになっているからです。貸借対照表上にはクラフト・ハインツ社の株式分として、GAAP準拠の数字で176億ドルを計上しています。一方でその市場価格は253億ドル、取得原価は98億ドルでした。
* バークシャーの子会社各社が設立している年金基金が保有する株式は除きます。
** この数字は実際の購入価格であり、税額計算時の基礎となるものです。一方、GAAP上の「費用」はいくつかの点で異なっています。GAAPの規則では減損が要求されているからです。
上記の銘柄の中には、トッド・コームズあるいはテッド・ウェシュラーが手掛けているものも複数含まれています。彼らはわたしと共にバークシャーにおける投資業務を担当しています。二人ともわたしから独立しており、おのおのが120億ドル以上の資産を運用しています。毎月出してくれるポートフォリオの概略をみてから、彼らが下した決定を知ることもよくあります。彼らの運用資産は合算すると250億ドルですが、そのなかにはバークシャーの一部の子会社が設立している年金からの受託分、80億ドル超が含まれています。上述したように、年金における投資分はバークシャーの持ち株を示した上の表には含まれていません。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
チャーリーとわたしは、バークシャーが保有している普通株のことを、市場で取引されているものではありますが、発行元企業の所有権だとみなしています。「株価チャート」の形状や、アナリストが発表する「目標」株価や、メディアに登場する解説者の意見、そういったものに基づいて売買するための「単なる銘柄コード」、とは考えていません。そうではなく、投資先の事業が成功を収めれば(ほとんどはそうなると信じていますが)、わたしたちがした投資も同じように成功を収める、と確信しているだけです。その見返りがそこそこで終わることもあるでしょう。逆に、キャッシュ・レジスターが鳴り響いて止まないこともあるでしょう。あるいは、手痛い失敗をすることもあると思います。しかし全体としてみれば、いずれはかなりの成果を手にできるはずです。米国では、株式に投資する者には追い風が吹いているのです。
当社の株式ポートフォリオ、これを「さまざまな公開企業に分散させた『少数株主としての所有権』」と称しますが、そこからバークシャーが2017年に受け取った配当金は37億ドルになりました。この数字はGAAP準拠の報告値に含まれていますし、四半期及び年次報告で言及している「営業利益」にも含まれています。
しかしその配当金の金額では、当社の保有株式から生まれ出る「真の」利益を十全にはとらえていません。「株主に関する事業上の原則」を何十年にもわたって掲載してきましたが(年次報告書19ページ)、その原則6で次のように記しています。「投資先企業があげた利益のうち内部留保されたものは、少なくとも同じ金額がキャピタル・ゲインの形で将来還元されることを期待する」と。
GAAPで定められた新たな規則によって、未実現損益を毎回の会計報告に記載するように強制されたこともあり、当社における譲渡益(及び損失)の認識額には波が生じると思います。しかし当社の投資先が留保する利益は、それらをひとまとまりとして捉えれば、いずれはそれ相応のキャピタル・ゲインの形でバークシャーに還元される、と確信しています。
上述してきた「価値の蓄積」と「留保利益」のつながりは、短期的には感知できないと思います。株価とは、年ごとに蓄積される本来的な価値にはどうやら縛られずに、騰落するものです。しかしやがては、度々引用されてきたベン・グレアムの格言が、真実だったとわかる日がきます。「短期でみれば、市場とは投票機である。しかし長期になれば、秤量機に変わる」日が。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
(この節、次回につづく)
Investments
Below we list our fifteen common stock investments that at yearend had the largest market value. We exclude our Kraft Heinz holding - 325,442,152 shares - because Berkshire is part of a control group and therefore must account for this investment on the “equity” method. On its balance sheet, Berkshire carries its Kraft Heinz holding at a GAAP figure of $17.6 billion. The shares had a yearend market value of $25.3 billion, and a cost basis of $9.8 billion.
[The table is omitted by the blog author.]
* Excludes shares held by pension funds of Berkshire subsidiaries.
** This is our actual purchase price and also our tax basis; GAAP “cost” differs in a few cases because of write-downs that have been required under GAAP rules.
Some of the stocks in the table are the responsibility of either Todd Combs or Ted Weschler, who work with me in managing Berkshire’s investments. Each, independently of me, manages more than $12 billion; I usually learn about decisions they have made by looking at monthly portfolio summaries. Included in the $25 billion that the two manage is more than $8 billion of pension trust assets of certain Berkshire subsidiaries. As noted, pension investments are not included in the preceding tabulation of Berkshire holdings.
* * * * * * * * * * * *
Charlie and I view the marketable common stocks that Berkshire owns as interests in businesses, not as ticker symbols to be bought or sold based on their “chart” patterns, the “target” prices of analysts or the opinions of media pundits. Instead, we simply believe that if the businesses of the investees are successful (as we believe most will be) our investments will be successful as well. Sometimes the payoffs to us will be modest; occasionally the cash register will ring loudly. And sometimes I will make expensive mistakes. Overall - and over time - we should get decent results. In America, equity investors have the wind at their back.
From our stock portfolio - call our holdings “minority interests” in a diversified group of publicly-owned businesses - Berkshire received $3.7 billion of dividends in 2017. That’s the number included in our GAAP figures, as well as in the “operating earnings” we reference in our quarterly and annual reports.
That dividend figure, however, far understates the “true” earnings emanating from our stock holdings. For decades, we have stated in Principle 6 of our “Owner-Related Business Principles” (page 19) that we expect undistributed earnings of our investees to deliver us at least equivalent earnings by way of subsequent capital gains.
Our recognition of capital gains (and losses) will be lumpy, particularly as we conform with the new GAAP rule requiring us to constantly record unrealized gains or losses in our earnings. I feel confident, however, that the earnings retained by our investees will over time, and with our investees viewed as a group, translate into commensurate capital gains for Berkshire.
The connection of value-building to retained earnings that I’ve just described will be impossible to detect in the short term. Stocks surge and swoon, seemingly untethered to any year-to-year buildup in their underlying value. Over time, however, Ben Graham’s oft-quoted maxim proves true: “In the short run, the market is a voting machine; in the long run, however, it becomes a weighing machine.”
* * * * * * * * * * * *
2018年3月2日金曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(5)定番の教え:株式投資の捉えかた
2017年度「バフェットからの手紙」から、バークシャーが手がけている投資について触れた節をご紹介します。今回分の後半はウォーレンの主張としておなじみの内容ですが、読むたびに姿勢を正される気がします。前回分はこちらです。(日本語は拙訳)

0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿