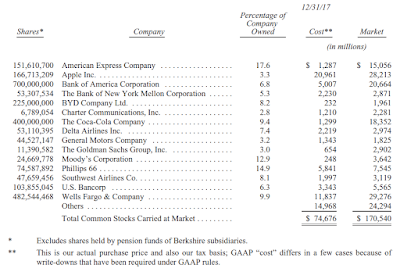
投資の状況について
以下の表は、当社が投資した普通株のうち、年末時点で市場評価額が大きかった15件を並べたものです。ただしクラフト・ハインツ社の3億2,544万2,152株は含んでいません。バークシャーは同社の支配会社に名を連ねているので、「持分」法によって会計報告することになっているからです。貸借対照表上にはクラフト・ハインツ社の株式分として、GAAP準拠の数字で176億ドルを計上しています。一方でその市場価格は253億ドル、取得原価は98億ドルでした。
* バークシャーの子会社各社が設立している年金基金が保有する株式は除きます。
** この数字は実際の購入価格であり、税額計算時の基礎となるものです。一方、GAAP上の「費用」はいくつかの点で異なっています。GAAPの規則では減損が要求されているからです。
上記の銘柄の中には、トッド・コームズあるいはテッド・ウェシュラーが手掛けているものも複数含まれています。彼らはわたしと共にバークシャーにおける投資業務を担当しています。二人ともわたしから独立しており、おのおのが120億ドル以上の資産を運用しています。毎月出してくれるポートフォリオの概略をみてから、彼らが下した決定を知ることもよくあります。彼らの運用資産は合算すると250億ドルですが、そのなかにはバークシャーの一部の子会社が設立している年金からの受託分、80億ドル超が含まれています。上述したように、年金における投資分はバークシャーの持ち株を示した上の表には含まれていません。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
チャーリーとわたしは、バークシャーが保有している普通株のことを、市場で取引されているものではありますが、発行元企業の所有権だとみなしています。「株価チャート」の形状や、アナリストが発表する「目標」株価や、メディアに登場する解説者の意見、そういったものに基づいて売買するための「単なる銘柄コード」、とは考えていません。そうではなく、投資先の事業が成功を収めれば(ほとんどはそうなると信じていますが)、わたしたちがした投資も同じように成功を収める、と確信しているだけです。その見返りがそこそこで終わることもあるでしょう。逆に、キャッシュ・レジスターが鳴り響いて止まないこともあるでしょう。あるいは、手痛い失敗をすることもあると思います。しかし全体としてみれば、いずれはかなりの成果を手にできるはずです。米国では、株式に投資する者には追い風が吹いているのです。
当社の株式ポートフォリオ、これを「さまざまな公開企業に分散させた『少数株主としての所有権』」と称しますが、そこからバークシャーが2017年に受け取った配当金は37億ドルになりました。この数字はGAAP準拠の報告値に含まれていますし、四半期及び年次報告で言及している「営業利益」にも含まれています。
しかしその配当金の金額では、当社の保有株式から生まれ出る「真の」利益を十全にはとらえていません。「株主に関する事業上の原則」を何十年にもわたって掲載してきましたが(年次報告書19ページ)、その原則6で次のように記しています。「投資先企業があげた利益のうち内部留保されたものは、少なくとも同じ金額がキャピタル・ゲインの形で将来還元されることを期待する」と。
GAAPで定められた新たな規則によって、未実現損益を毎回の会計報告に記載するように強制されたこともあり、当社における譲渡益(及び損失)の認識額には波が生じると思います。しかし当社の投資先が留保する利益は、それらをひとまとまりとして捉えれば、いずれはそれ相応のキャピタル・ゲインの形でバークシャーに還元される、と確信しています。
上述してきた「価値の蓄積」と「留保利益」のつながりは、短期的には感知できないと思います。株価とは、年ごとに蓄積される本来的な価値にはどうやら縛られずに、騰落するものです。しかしやがては、度々引用されてきたベン・グレアムの格言が、真実だったとわかる日がきます。「短期でみれば、市場とは投票機である。しかし長期になれば、秤量機に変わる」日が。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
(この節、次回につづく)
Investments
Below we list our fifteen common stock investments that at yearend had the largest market value. We exclude our Kraft Heinz holding - 325,442,152 shares - because Berkshire is part of a control group and therefore must account for this investment on the “equity” method. On its balance sheet, Berkshire carries its Kraft Heinz holding at a GAAP figure of $17.6 billion. The shares had a yearend market value of $25.3 billion, and a cost basis of $9.8 billion.
[The table is omitted by the blog author.]
* Excludes shares held by pension funds of Berkshire subsidiaries.
** This is our actual purchase price and also our tax basis; GAAP “cost” differs in a few cases because of write-downs that have been required under GAAP rules.
Some of the stocks in the table are the responsibility of either Todd Combs or Ted Weschler, who work with me in managing Berkshire’s investments. Each, independently of me, manages more than $12 billion; I usually learn about decisions they have made by looking at monthly portfolio summaries. Included in the $25 billion that the two manage is more than $8 billion of pension trust assets of certain Berkshire subsidiaries. As noted, pension investments are not included in the preceding tabulation of Berkshire holdings.
* * * * * * * * * * * *
Charlie and I view the marketable common stocks that Berkshire owns as interests in businesses, not as ticker symbols to be bought or sold based on their “chart” patterns, the “target” prices of analysts or the opinions of media pundits. Instead, we simply believe that if the businesses of the investees are successful (as we believe most will be) our investments will be successful as well. Sometimes the payoffs to us will be modest; occasionally the cash register will ring loudly. And sometimes I will make expensive mistakes. Overall - and over time - we should get decent results. In America, equity investors have the wind at their back.
From our stock portfolio - call our holdings “minority interests” in a diversified group of publicly-owned businesses - Berkshire received $3.7 billion of dividends in 2017. That’s the number included in our GAAP figures, as well as in the “operating earnings” we reference in our quarterly and annual reports.
That dividend figure, however, far understates the “true” earnings emanating from our stock holdings. For decades, we have stated in Principle 6 of our “Owner-Related Business Principles” (page 19) that we expect undistributed earnings of our investees to deliver us at least equivalent earnings by way of subsequent capital gains.
Our recognition of capital gains (and losses) will be lumpy, particularly as we conform with the new GAAP rule requiring us to constantly record unrealized gains or losses in our earnings. I feel confident, however, that the earnings retained by our investees will over time, and with our investees viewed as a group, translate into commensurate capital gains for Berkshire.
The connection of value-building to retained earnings that I’ve just described will be impossible to detect in the short term. Stocks surge and swoon, seemingly untethered to any year-to-year buildup in their underlying value. Over time, however, Ben Graham’s oft-quoted maxim proves true: “In the short run, the market is a voting machine; in the long run, however, it becomes a weighing machine.”
* * * * * * * * * * * *
2018年3月2日金曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(5)定番の教え:株式投資の捉えかた
2017年度「バフェットからの手紙」から、バークシャーが手がけている投資について触れた節をご紹介します。今回分の後半はウォーレンの主張としておなじみの内容ですが、読むたびに姿勢を正される気がします。前回分はこちらです。(日本語は拙訳)
2018年3月1日木曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(4)バフェットらしいあざやかな教訓
2017年度「バフェットからの手紙」から、「賭け」の話題は今回でおわりです。前回分はこちらです。(日本語は拙訳)
最初の印象で「あっさり」と書きましたが、表面的な読み方ゆえの感想でした。くりかえし読むほどに、教訓や人生哲学やさまざまな教えが読み取れ、あいかわらず勉強になる文章だと感じるようになりました。なお、他の節もひきつづき取り上げるつもりです。
投資という行動には、「将来になってからもっと多くの消費ができるように、今日の消費を辛抱すること」が含まれます。「リスク」とは、この目的が達成できない可能性を指す言葉です。
その基準に従えば、「無リスク」とされていた長期債へ2012年の時点で投資するのは、普通株に長期投資するよりもずっとリスキーな選択でした。2012年から2017年にかけてのインフレ率が年間1%だとしても、プロテジェとわたしが手放した米国債の購買力は減っていたでしょう。
ただし早々に申し上げておきたいのですが、「明日や来週、あるいは来年であってさえも、短期の国内債券とくらべると株式のほうがリスキーである」ことは、たしかにそのとおりです。はるかにリスキーです。しかし投資期間が長期になるにつれ、米国株からなる分散されたポートフォリオのリスクは、債券よりも累進的に小さくなっていきます。ただし、「その時点での金利と比較して妥当な株価収益率で株式を買うこと」という条件が付きます。
長期的視野に基づいている投資家、たとえば年金基金や大学基金、倹約派の個人投資家は、投資上の「リスク」を量るために、ポートフォリオにおける債券対株式の比率を使うのは、たいへんな間違いです。ポートフォリオに含まれた質の高い債券でさえ、リスクを増加させることがしばしばあります。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
さて、わたしたちの果たした「賭け」から得られた最後の教訓になります。それは「大局的で『易しい』判断に付き従い、行動を慎むこと」です。10年にわたる賭けの間、[プロテジェ側が選択した]200名を超すヘッジ・ファンドのマネージャー諸氏が何万回と売買を繰り返したのは、ほぼ間違いないと思います。彼らのほとんどは判断を下す際に熟考し、どれもうまい一手だと信じていたのは、疑うところがないでしょう。投資の判断を下す前には、10-K[有価証券報告書]から学んだり、経営陣と対話したり、業界紙を読んだり、ウォール街のアナリストと意見交換をしたことでしょう。
一方プロテジェとわたしのほうは、調査や識見や才気のいずれに頼ることもなく、10年間でただ一度だけ、投資上の決定を下しました。保有していた債券を、100倍超になる利益倍率で(売却金額/利回り = 95.7/0.88)、売却すると決めただけでした。なおその際の「利益」とは、残りの5年間にわたって増加することのない値です。
売却後に手にする両者の資金は、バークシャーという名の単一の証券へと移ります。それはすなわち、多岐にわたる堅実な事業を保有したことになります。利益の留保分が使えるのですから、バークシャーの価値が年率8%に満たない成長にとどまるとは思えませんでした。たとえ景気がそこそこ程度だとしてもです。
このように幼稚園程度の分析が済んだところで、プロテジェとわたしは債券から株式への交換を実行し、一息つきました。いずれ8%が0.88%を上回るのは確実だろうと思っていました。それも「大幅に」ですよ。
(この節、おわり)
Investing is an activity in which consumption today is foregone in an attempt to allow greater consumption at a later date. “Risk” is the possibility that this objective won’t be attained.
By that standard, purportedly “risk-free” long-term bonds in 2012 were a far riskier investment than a long-term investment in common stocks. At that time, even a 1% annual rate of inflation between 2012 and 2017 would have decreased the purchasing-power of the government bond that Protege and I sold.
I want to quickly acknowledge that in any upcoming day, week or even year, stocks will be riskier - far riskier - than short-term U.S. bonds. As an investor’s investment horizon lengthens, however, a diversified portfolio of U.S. equities becomes progressively less risky than bonds, assuming that the stocks are purchased at a sensible multiple of earnings relative to then-prevailing interest rates.
It is a terrible mistake for investors with long-term horizons - among them, pension funds, college endowments and savings-minded individuals - to measure their investment “risk” by their portfolio’s ratio of bonds to stocks. Often, high-grade bonds in an investment portfolio increase its risk.
* * * * * * * * * * * *
A final lesson from our bet: Stick with big, “easy” decisions and eschew activity. During the ten-year bet, the 200-plus hedge-fund managers that were involved almost certainly made tens of thousands of buy and sell decisions. Most of those managers undoubtedly thought hard about their decisions, each of which they believed would prove advantageous. In the process of investing, they studied 10-Ks, interviewed managements, read trade journals and conferred with Wall Street analysts.
Protege and I, meanwhile, leaning neither on research, insights nor brilliance, made only one investment decision during the ten years. We simply decided to sell our bond investment at a price of more than 100 times earnings (95.7 sale price/.88 yield), those being “earnings” that could not increase during the ensuing five years.
We made the sale in order to move our money into a single security - Berkshire - that, in turn, owned a diversified group of solid businesses. Fueled by retained earnings, Berkshire’s growth in value was unlikely to be less than 8% annually, even if we were to experience a so-so economy.
After that kindergarten-like analysis, Protege and I made the switch and relaxed, confident that, over time, 8% was certain to beat .88%. By a lot.
最初の印象で「あっさり」と書きましたが、表面的な読み方ゆえの感想でした。くりかえし読むほどに、教訓や人生哲学やさまざまな教えが読み取れ、あいかわらず勉強になる文章だと感じるようになりました。なお、他の節もひきつづき取り上げるつもりです。
2018年2月28日水曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(3)バカだねと思われることが必要なとき
2017年度「バフェットからの手紙」から、前回に続いて「賭け」の話題です。(日本語は拙訳)
最終的な「賭け」の結果は、次のようになりました。
暦年 ファンドA ファンドB ファンドC ファンドD ファンドE S&Pファンド 2008 -16.5% -22.3% -21.3% -29.3% -30.1% -37.0% 2009 11.3% 14.5% 21.4% 16.5% 16.8% 26.6% 2010 5.9% 6.8% 13.3% 4.9% 11.9% 15.1% 2011 -6.3% -1.3% 5.9% -6.3% -2.8% 2.1% 2012 3.4% 9.6% 5.7% 6.2% 9.1% 16.0% 2013 10.5% 15.2% 8.8% 14.2% 14.4% 32.3% 2014 4.7% 4.0% 18.9% 0.7% -2.1% 13.6% 2015 1.6% 2.5% 5.4% 1.4% -5.0% 1.4% 2016 -3.2% 1.9% -1.7% 2.5% 4.4% 11.9% 2017 12.2% 10.6% 15.6% N/A 18.0% 21.8% 累計 21.7% 42.3% 87.7% 2.8% 27.0% 125.8% 年率 2.0% 3.6% 6.5% 0.3% 2.4% 8.5%
(注)プロテジェ・パートナーズとの合意によって、各ファンド・オブ・ファンズの名称は非公開としました。ただしわたし自身は、年次監査報告を受け取っています。なお2016年のファンドA・B・Cの数字は、昨年記載した内容から若干改訂しました。またファンドDは2017年中に解散したため、年間損益率の平均値は運営されていた9年間の成績をもとに算出してあります。
5本のファンド・オブ・ファンズは素早い駆け出しをみせ、2008年にはどれもがインデックス・ファンドを負かしました。しかしその後はまるでうまくいきませんでした。つづく9年間はどの年も、ファンド・オブ・ファンズ全体としてみればインデックス・ファンドから遅れを取ったのです。
あえて申し上げておきますが、その10年の間で株式市場の動向に異例なところは何もありませんでした。2007年の終わりごろに投資の「専門家」各氏に依頼して、普通株の長期的収益率を予想してもらえば、その平均値は8.5%に近い数字になったでしょう。これはS&P500が実際に記録した数字です。そのような環境であれば、儲けをあげるのは易しいことです。実際のところ、ウォール街の「助力者」たちが手にした総額は、びっくり仰天の金額でした。しかしながらその人たちが大いに潤った一方で、彼らに資金を投じた多くの投資家にとっては、失われた10年間となりました。
投資の成績はたゆたうものですが、手数料を遠慮されることはありません。
* * * * * * * * * * * *
今回の「賭け」によって、投資におけるもうひとつの重要な教訓があらわになりました。市場はおおむね合理的ですが、ときにおかしな行動をとります。その際に現れる機会をつかむには、まばゆい知性は必要ありません。経済学の学位も、アルファやベータといったウォール街で使われる専門用語になじんでいる必要もありません。そうではなく投資家に必要なのは、群集心理にみられる恐怖や熱狂から距離をおき、一握りの単純なファンダメンタルを凝視できる力です。かなりの期間にわたって、平凡と思われたりあるいはアホとさえ思われたりする道を、あえて選べる心持ちも欠かせません。
プロテジェとわたしは当初、最終的に必要な100万ドルを用意するために、財務省発行の額面50万ドルの割引債(ストリップスと呼ばれることがあります)をそれぞれ購入しました。その債券を買う価格が、それぞれ31万8,250ドルだったのです。これは1ドルに対して64セントを若干下回る値段でした。この金額を払うことで、10年後に50万ドルずつを受け取る算段でした。
その名称からおわかりになると思いますが、両者が買った債券には利子が支払われません。しかし(割り引いた値段で購入しているため)、満期まで保有すれば年率にして4.56%の利益が得られます。当初は年ごとに得られるリターンだけを考えており、2017年末に債券が満期を迎えることで、賭けの勝者側が指定する慈善先に100万ドルを贈るつもりでした。
しかし購入した後になって、債券市場で実に奇妙なことが起こりました。2012年の11月に、満期日まで残り5年ほどとなったわたしたちの債券が、額面価格の95.7%で買われていたのです。その値段になると、満期までの利回りは年率1%以下でした。正確には0.88%でした。
なんとも貧相なリターンなので、わたしたちが債券に投資していることが、米国株に投資するのとくらべてひどく間抜けなように思えました。S&P500であれば、すなわちそれは「米国におけるビジネスを時価総額によって適宜重みづけした大断面」のようなものですが、株主資本(つまり純資産)利益率にして年率10%を大きく上回る稼ぎを、長期間にわたってあげてきたのですから。
2012年11月、つまりわたしたちがこの件を考え直した時点で、S&P500に投資することで受け取れる配当金のリターンは年率2.5%、つまりわたしたちが購入した財務省証券の利回りの約3倍でした。しかも配当金が増額されていくのは、まず間違いないと言えました。それだけではなく、500社を構成する各社は莫大な資金を留保していました。各社はその資金を使って事業を拡大したり、よくあるように自社株を買い戻すことでしょう。どちらであろうと、いずれは1株当たり利益を大幅に増加させるはずです。1776年以来いつもそうだったように、いかなる困難な時期が来ようと、米国経済は前進し続けてきたのです。
2012年の末に債券と株式の間で評価の釣り合いが大幅に乱れたことで、プロテジェとわたしは次の点を合意しました。「両者が購入した債券を当初の予定より5年早く売却し、得られた資金でバークシャーのB株を11,200株買うこと」です。その結果、ガールズ・インクのオマハ事務所が先月受け取った金額は、当初望まれていた100万ドルではなく、222万2,279ドルとなりました。
お断りしておきますが、2012年に債券から乗り換えた後のバークシャーが、きわだった業績を残したわけではありません。しかし傑出する必要はなかったのです。結局のところ、バークシャー株からあがる利益が、年間利回り0.88%の債券に勝てばいいだけのことでした。獅子奮迅の働きは不要でした。
債券をバークシャー株に交換することの唯一のリスクは、2017年末の株式市場が極端に弱い事態にめぐり合ってしまうことでした。しかしその可能性は非常に小さい(いつであろうといくらかは存在します)だろうと、両者ともに考えていました。そう結論付けた理由は2つあります。ひとつめは、2012年末のバークシャー株が妥当な値段だったことです。ふたつめは、「賭け」が終わりとなるまでの5年間のうちに、バークシャーがほぼ確実に資産を大幅に蓄積させると考えられたからです。ただし、そうではあっても交換によって生じる、今回の慈善に関するあらゆるリスクを排除するために、2017年末にバークシャーの11,200株を売却しても100万ドルに満たない場合には、わたしが不足分を埋め合わせる旨、合意しました。(PDFファイル11ページ目)
(この節、まだつづきます)
Here’s the final scorecard for the bet:
[The performance chart is omitted by the blog author.]
Footnote: Under my agreement with Protege Partners, the names of these funds-of-funds have never been publicly disclosed. I, however, have received their annual audits from Protege. The 2016 figures for funds A, B and C were revised slightly from those originally reported last year. Fund D was liquidated in 2017; its average annual gain is calculated for the nine years of its operation.
The five funds-of-funds got off to a fast start, each beating the index fund in 2008. Then the roof fell in. In every one of the nine years that followed, the funds-of-funds as a whole trailed the index fund.
Let me emphasize that there was nothing aberrational about stock-market behavior over the ten-year stretch. If a poll of investment “experts” had been asked late in 2007 for a forecast of long-term common-stock returns, their guesses would have likely averaged close to the 8.5% actually delivered by the S&P 500. Making money in that environment should have been easy. Indeed, Wall Street “helpers” earned staggering sums. While this group prospered, however, many of their investors experienced a lost decade.
Performance comes, performance goes. Fees never falter.
* * * * * * * * * * * *
The bet illuminated another important investment lesson: Though markets are generally rational, they occasionally do crazy things. Seizing the opportunities then offered does not require great intelligence, a degree in economics or a familiarity with Wall Street jargon such as alpha and beta. What investors then need instead is an ability to both disregard mob fears or enthusiasms and to focus on a few simple fundamentals. A willingness to look unimaginative for a sustained period - or even to look foolish - is also essential.
Originally, Protege and I each funded our portion of the ultimate $1 million prize by purchasing $500,000 face amount of zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds (sometimes called “strips”). These bonds cost each of us $318,250 - a bit less than 64¢ on the dollar - with the $500,000 payable in ten years.
As the name implies, the bonds we acquired paid no interest, but (because of the discount at which they were purchased) delivered a 4.56% annual return if held to maturity. Protege and I originally intended to do no more than tally the annual returns and distribute $1 million to the winning charity when the bonds matured late in 2017.
After our purchase, however, some very strange things took place in the bond market. By November 2012, our bonds - now with about five years to go before they matured - were selling for 95.7% of their face value. At that price, their annual yield to maturity was less than 1%. Or, to be precise, .88%.
Given that pathetic return, our bonds had become a dumb - a really dumb - investment compared to American equities. Over time, the S&P 500 - which mirrors a huge cross-section of American business, appropriately weighted by market value - has earned far more than 10% annually on shareholders’ equity (net worth).
In November 2012, as we were considering all this, the cash return from dividends on the S&P 500 was 2.5% annually, about triple the yield on our U.S. Treasury bond. These dividend payments were almost certain to grow. Beyond that, huge sums were being retained by the companies comprising the 500. These businesses would use their retained earnings to expand their operations and, frequently, to repurchase their shares as well. Either course would, over time, substantially increase earnings-per-share. And - as has been the case since 1776 - whatever its problems of the minute, the American economy was going to move forward.
Presented late in 2012 with the extraordinary valuation mismatch between bonds and equities, Protege and I agreed to sell the bonds we had bought five years earlier and use the proceeds to buy 11,200 Berkshire “B” shares. The result: Girls Inc. of Omaha found itself receiving $2,222,279 last month rather than the $1 million it had originally hoped for.
Berkshire, it should be emphasized, has not performed brilliantly since the 2012 substitution. But brilliance wasn’t needed: After all, Berkshire’s gain only had to beat that annual .88% bond bogey - hardly a Herculean achievement.
The only risk in the bonds-to-Berkshire switch was that yearend 2017 would coincide with an exceptionally weak stock market. Protege and I felt this possibility (which always exists) was very low. Two factors dictated this conclusion: The reasonable price of Berkshire in late 2012, and the large asset build-up that was almost certain to occur at Berkshire during the five years that remained before the bet would be settled. Even so, to eliminate all risk to the charities from the switch, I agreed to make up any shortfall if sales of the 11,200 Berkshire shares at yearend 2017 didn’t produce at least $1 million.
2018年2月27日火曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(2)10年越しの賭けの結果
2017年度「バフェットからの手紙」からの引用が続きます。今回からの話題は、ウォーレンが前年度にとりあげた「賭け」の続きです(日本語は拙訳)。やはり今回も、この話題が一般(=非株主)向けのメイン・テーマだと思います。本シリーズの前回分投稿はこちらです。
なお、前年度分を紹介した投稿は以下のとおりです。未読の方は先に読まれることをお勧めします。
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(3)100歳になっても生きているだろうか
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(4)S&P500ファンドの威力
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(5)手数料は眠らない
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(6)アクティブ勢VSパッシブ勢
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(7)あのサルのように運が良ければ
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(8)金持ちはどう感じているのか
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(9)金持ちが熟練者と出会うとき
なお、前年度分を紹介した投稿は以下のとおりです。未読の方は先に読まれることをお勧めします。
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(3)100歳になっても生きているだろうか
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(4)S&P500ファンドの威力
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(5)手数料は眠らない
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(6)アクティブ勢VSパッシブ勢
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(7)あのサルのように運が良ければ
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(8)金持ちはどう感じているのか
・2016年度バフェットからの手紙(9)金持ちが熟練者と出会うとき
終わりをむかえた「例の賭け」から得られた、投資に関する意外な教訓
2007年12月19日にわたしが始めた10年越しの賭けについて、9割がた進んだ昨年の段階で、詳細な報告をしました(年次報告書に含めたその全文は、今回の年次報告書[PDF]の24-26ページに再掲してあります)。そして今では最終的な数字がそろいました。さまざまな観点において目を見張る結果でした。
賭けを始めた理由は2つありました。ひとつめは、わたしが拠出する31万8,250ドルをもとに、不相応なほど大きな金額に増やしたかったためです。わたしの予想する通りにものごとが進めば、2018年の初めにガールズ・インクのオマハ事務所へ寄付されることになる資金です。ふたつめは、わたしが確信していることを広く知ってもらいたかったからです。つまりそれは、「アクティブな運用者が関わらないS&P500のインデックス・ファンドを選ぶことで、実質的に費用のかからない投資となるわたしのやりかたが、ほとんどの資産運用のプロよりも優れた成績を、いずれは達成する」という考えです。ただしその「助力者」たる方々は、敬意を払われた上に、金銭面での見返りも厚遇されるとは思いますが。
この問題に取り組むことには、はなはだしく重要な意味があります。米国の投資家は毎年多額の費用を投資助言者へ支払っています。さまざまな階層にわたるがゆえの費用が課されることもよくあります。そのような投資家を全体としてとらえたときに、はたして支払った金額にふさわしい対価を受けているのでしょうか。実際のところ、助言者に対する総支出に対してなにかを受け取っているのでしょうか。
賭けの相手となったプロテジェ・パートナーズはS&P500の成績を上回ることをねらって、5本の「ファンド・オブ・ファンズ」を選択しました。彼らが選んだこの数が、少ないということはありません。ファンド・オブ・ファンズを5本選んだということは、結局のところ200本のヘッジ・ファンドへ投資することになったからです。
ウォール街では投資助言会社として知られているプロテジェは、実質的に5名の投資専門家を選んだことになります。さらには各々がヘッジ・ファンドを運営している、投資の専門家を数百名抱えたことになります。これは、「頭脳とアドレナリンと自信に満ちたエリートからなる要員のそろった集団」ということになります。
5本のファンド・オブ・ファンズそれぞれを運営するマネージャーには、さらに有利な点がありました。みずからのポートフォリオに含まれているヘッジ・ファンドを、10年の間に入れ替えることができた点です。実際のところ彼らは、新たな「スター」へ資金を投下し、その一方で運用者の神通力が失われたヘッジ・ファンドからは資金を引き揚げました。
プロテジェ側の役者諸氏は、成功に対する大きな見返りを約束されていました。ファンド・オブ・ファンズの運営者だけでなく、選択された各ヘッジ・ファンドの運営者も、儲けの大幅な部分が分配されることになっていたのです。たとえそれが単に市場全体が上昇したときであっても、です。(わたしたちがバークシャーを経営し始めた以降で10年にわたる期間を考えたとき、1年ずつずらすと都合43回ありましたが、S&P500はそのすべてにおいて、プラスだった年数がマイナスだった年数を上回りました)
成功に応じて受けられるそういった見返りは、本来は強調すべきところを、おいしくて巨大なケーキの上に塗り伸ばされていました。たとえファンドが10年の間に投資家の資金を失ったとしても、運用者諸氏は大金持ちになることができたでしょう。資産額に対する割合が、平均にして「驚きの2.5%前後」にのぼる固定手数料を、ファンド・オブ・ファンズへ投資する者が毎年支払うとなれば、それも実現する話です。その手数料の一部はファンド・オブ・ファンズ5本の各運用者へ、そして残りは下位にあたるヘッジ・ファンドの200名超にのぼる運用者へとわたったのです。(PDFファイル10ページ目)
(この節、つづく)
“The Bet” is Over and Has Delivered an Unforeseen Investment Lesson
Last year, at the 90% mark, I gave you a detailed report on a ten-year bet I had made on December 19, 2007. (The full discussion from last year’s annual report is reprinted on pages 24 - 26.) Now I have the final tally - and, in several respects, it’s an eye-opener.
I made the bet for two reasons: (1) to leverage my outlay of $318,250 into a disproportionately larger sum that - if things turned out as I expected - would be distributed in early 2018 to Girls Inc. of Omaha; and (2) to publicize my conviction that my pick - a virtually cost-free investment in an unmanaged S&P 500 index fund - would, over time, deliver better results than those achieved by most investment professionals, however well-regarded and incentivized those “helpers” may be.
Addressing this question is of enormous importance. American investors pay staggering sums annually to advisors, often incurring several layers of consequential costs. In the aggregate, do these investors get their money’s worth? Indeed, again in the aggregate, do investors get anything for their outlays?
Protege Partners, my counterparty to the bet, picked five “funds-of-funds” that it expected to overperform the S&P 500. That was not a small sample. Those five funds-of-funds in turn owned interests in more than 200 hedge funds.
Essentially, Protege, an advisory firm that knew its way around Wall Street, selected five investment experts who, in turn, employed several hundred other investment experts, each managing his or her own hedge fund. This assemblage was an elite crew, loaded with brains, adrenaline and confidence.
The managers of the five funds-of-funds possessed a further advantage: They could - and did - rearrange their portfolios of hedge funds during the ten years, investing with new “stars” while exiting their positions in hedge funds whose managers had lost their touch.
Every actor on Protege’s side was highly incentivized: Both the fund-of-funds managers and the hedge-fund managers they selected significantly shared in gains, even those achieved simply because the market generally moves upwards. (In 100% of the 43 ten-year periods since we took control of Berkshire, years with gains by the S&P 500 exceeded loss years.)
Those performance incentives, it should be emphasized, were frosting on a huge and tasty cake: Even if the funds lost money for their investors during the decade, their managers could grow very rich. That would occur because fixed fees averaging a staggering 2.5% of assets or so were paid every year by the fund-of-funds’ investors, with part of these fees going to the managers at the five funds-of-funds and the balance going to the 200-plus managers of the underlying hedge funds.
2018年2月26日月曜日
2017年度バフェットからの手紙(1)減税及び会計基準変更による影響
バークシャー・ハサウェイのウォーレン・バフェットが、2/24(土)付けで2017年度の「バフェットからの手紙」を公開しています。今回は全16ページと、少なくとも今世紀に入ってから最も短いレターです。一読した印象も「地味であっさり」といったところですが、よく考えれば大切な文章も当然ながら見受けられます。これからまじめに読み込むつもりです。
今回は冒頭の文章から、拙訳付きでご紹介します。言葉通り、バークシャーの株主に向けた話題です。
SHAREHOLDER LETTER 2017 [PDF] (Berkshire Hathaway)
今回は冒頭の文章から、拙訳付きでご紹介します。言葉通り、バークシャーの株主に向けた話題です。
SHAREHOLDER LETTER 2017 [PDF] (Berkshire Hathaway)
バークシャー・ハサウェイの株主のみなさんへ、
2017年度において、バークシャーの純資産は653億ドル増加しました。その結果、クラスA株及びクラスB株のいずれにおいても、1株当たりの簿価は23%増えています。過去53年間において(すなわち現経営陣が就任した後のことですが)、1株当たりの簿価は19ドルから21万1,750ドルに増加しました。これは年率にして19.1%の増加率になります。
巻頭にあげた[業績推移の]表は、30年間にわたって同じ書式を使ってきました。しかし2017年度は、これまでのお決まりから大きく逸脱しています。バークシャー内で達成したこと以外のものが、当社利益の大幅な部分を占めたからです。
そうではあるものの、650億ドルになる利益は現実のものですから、ご安心ください。ただし、バークシャー自身の活動によって得た金額は、360億ドルにとどまっています。残りの290億ドルは、議会が連邦税法を改定したことによって、12月にもたらされたものです。(税務的な面によってバークシャーが得た利益に関する詳細は、年次報告書のK32やK-89~K-90ページをご参照ください)
そのような財務上の事実があることをお断りしましたので、早速バークシャーの経営状況についてご説明したいと思います。しかし、もう1件だけお待ちください。GAAP(米国会計基準)に規定された新たな会計基準について、触れておかねばならないからです。この改定によって今後提出される四半期及び年次の会計報告では、バークシャーの純利益の数字が大幅に変形したものとなります。それによってメディアに登場する解説者や投資家が誤解してしまうことが、たびたび生じると思われます。
新たな規則は、「株式投資における未実現損益の期間増減額を、純利益の数字へ含めて報告書に記載しなければならない」点を要求しています。そのことで、GAAPに準拠する当社の経営成績は、実に荒々しく気まぐれに変動することになるでしょう。バークシャーは市場で取引されている株式を1,700億ドル保有しています(ただしクラフト・ハインツ社の当社持ち分を除く)。それら持ち株の評価額は、四半期ごとの会計期間において100億ドル以上容易に変動します。そのような規模で旋回する数字を報告利益に加えることは、当社の営業成績を描き出すまさしく重要な数字を台無しにします。バークシャーが示す「稼ぎ」は、分析しようにも役に立たないものとなるでしょう。
この新たな規則によって、コミュニケーション上の問題も併せて生じます。この問題は以前からも存在していました。「[証券売却時の]実現損益を当社の純利益に含めるように」と、会計規則が強制していたからです。そのため、過去の四半期及び年度ごとの決算発表の際には、「それらの実現益には気を取られないように」とみなさんに常々警告してきました。なぜならば未実現損益と同様に、その数字も不規則に変動するからです。
証券を売却した理由の大半は、その時期にそうするのが賢明だと思えたからでした。「なんとかして報告利益に影響させたい」と考えたわけではありません。その結果、ポートフォリオ全体が残念な成績の間に大幅な実現益を計上したことが、当社では往々にしてありました(その反対もありました)。
未実現益に関する新たな規則は、実現益に適用されている現行の規則がもたらした歪曲を、一層悪化させると思われます。そのため、みなさんが納得のいく数字を得られるように、それに必要な調整値を四半期ごとに説明する労苦を、わたしたちは背負うことになります。しかし決算発表時に映像で流れる解説はたちまち反応を受けがちですし、新聞の見出しでは必ずと言っていいほど前年比でみたGAAP純利益の増減に焦点を当てています。その結果、メディアはときに数字を強調した報道を行い、多くの読者や視聴者を不必要に怖がらせたり、煽り立てたりします。
わたしたちはこの問題を緩和するために、「決算報告の発表時期を、金曜日の遅い時刻つまり市場が終了してから少し後、あるいは土曜日の早朝にする」との慣習をつづけたいと考えています。それによって市場が開く月曜日までに、みなさんが分析にかける時間をなるべく多くとれるようになり、また資産運用者たるプロの方々が自分たちの見解を含めた解説を配布する余裕ができるでしょう。そうだとしても、会計のことがチンプンカンプンな株主の間では、かなりの戸惑いが生じると思われます。
バークシャーがもっとも心を砕いていること、それは1株当たり調整後利益を生む力を増加させることです。その指標はわたしだけではなく、長きにわたるパートナーであるチャーリー・マンガーも傾注しています。またみなさんもそうであってほしい、と両名とも望んでいます。それでは、引き続いて2017年度の星取表を説明します。(PDFファイル2ページ目)
To the Shareholders of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.:
Berkshire’s gain in net worth during 2017 was $65.3 billion, which increased the per-share book value of both our Class A and Class B stock by 23%. Over the last 53 years (that is, since present management took over), per-share book value has grown from $19 to $211,750, a rate of 19.1% compounded annually.
The format of that opening paragraph has been standard for 30 years. But 2017 was far from standard: A large portion of our gain did not come from anything we accomplished at Berkshire.
The $65 billion gain is nonetheless real - rest assured of that. But only $36 billion came from Berkshire’s operations. The remaining $29 billion was delivered to us in December when Congress rewrote the U.S. Tax Code. (Details of Berkshire’s tax-related gain appear on page K-32 and pages K-89 - K-90.)
After stating those fiscal facts, I would prefer to turn immediately to discussing Berkshire’s operations. But, in still another interruption, I must first tell you about a new accounting rule - a generally accepted accounting principle (GAAP) - that in future quarterly and annual reports will severely distort Berkshire’s net income figures and very often mislead commentators and investors.
The new rule says that the net change in unrealized investment gains and losses in stocks we hold must be included in all net income figures we report to you. That requirement will produce some truly wild and capricious swings in our GAAP bottom-line. Berkshire owns $170 billion of marketable stocks (not including our shares of Kraft Heinz), and the value of these holdings can easily swing by $10 billion or more within a quarterly reporting period. Including gyrations of that magnitude in reported net income will swamp the truly important numbers that describe our operating performance. For analytical purposes, Berkshire’s “bottom-line” will be useless.
The new rule compounds the communication problems we have long had in dealing with the realized gains (or losses) that accounting rules compel us to include in our net income. In past quarterly and annual press releases, we have regularly warned you not to pay attention to these realized gains, because they - just like our unrealized gains - fluctuate randomly.
That’s largely because we sell securities when that seems the intelligent thing to do, not because we are trying to influence earnings in any way. As a result, we sometimes have reported substantial realized gains for a period when our portfolio, overall, performed poorly (or the converse).
With the new rule about unrealized gains exacerbating the distortion caused by the existing rules applying to realized gains, we will take pains every quarter to explain the adjustments you need in order to make sense of our numbers. But televised commentary on earnings releases is often instantaneous with their receipt, and newspaper headlines almost always focus on the year-over-year change in GAAP net income. Consequently, media reports sometimes highlight figures that unnecessarily frighten or encourage many readers or viewers.
We will attempt to alleviate this problem by continuing our practice of publishing financial reports late on Friday, well after the markets close, or early on Saturday morning. That will allow you maximum time for analysis and give investment professionals the opportunity to deliver informed commentary before markets open on Monday. Nevertheless, I expect considerable confusion among shareholders for whom accounting is a foreign language.
At Berkshire what counts most are increases in our normalized per-share earning power. That metric is what Charlie Munger, my long-time partner, and I focus on - and we hope that you do, too. Our scorecard for 2017 follows.
登録:
投稿 (Atom)